Energy Drinks: What You Should Know Before You Sip
Energy drinks have become a go-to for many looking to boost their alertness and get through long days. But what’s really behind these colorful cans? Let’s break down what energy drinks are made of, how they affect you, and why they’ve become so popular.
What’s Inside an Energy Drink?
Most energy drinks pack caffeine, sugar or sweeteners, and other ingredients like taurine, B vitamins, and sometimes herbal extracts. The caffeine amount varies but can sometimes be higher than a cup of coffee. This blend is designed to increase energy and focus quickly. Knowing exactly what’s inside helps you decide if it’s right for your body and lifestyle.
The Buzz Around Energy Drinks: Benefits and Concerns
People enjoy energy drinks because they deliver a fast pick-me-up. They’re handy before workouts, long work hours, or when you need to stay sharp. However, drinking too many can cause jitters, heart palpitations, or sleep problems—especially if you’re sensitive to caffeine. It’s smart to check labels, watch how much you consume, and avoid mixing them with alcohol.
Energy drinks are not one-size-fits-all. Some brands focus on low-calorie options while others mix in extra ingredients for sports performance. Remember, reading reviews and staying updated on trends can guide you to safer and better choices that suit your needs.
If you’re curious about new releases or want honest facts about energy drinks and their impact on health, Spam Energy offers insight that keeps it real and easy to follow. Whether you’re a longtime fan or just trying them out, keep your energy smart and safe.
Energy drinks aren't safe for everyone. Teens, people with heart conditions, pregnant women, and those on certain medications should avoid them. Learn who's at risk and what to drink instead.
Energy drinks aren't just caffeinated beverages-they're specially formulated with stimulants like taurine, guarana, and high-dose B-vitamins to boost performance. Learn what truly qualifies as an energy drink and why most athletes avoid them.
Drinking a gallon of water a day sounds healthy, but it can be dangerous. Learn what science says about hydration, overhydration, and why energy drinks don’t make water intake safer - or smarter.
Most pro athletes avoid Red Bull due to its high sugar content and lack of performance benefits. Learn what they actually drink for energy, why caffeine works better in capsule form, and how to fuel like a pro without the hype.
NFL players avoid energy drinks during the season due to health risks and team policies. Instead, they rely on electrolyte solutions, black coffee, and science-backed recovery tools. Here’s what actually fuels them on and off the field.
Sports drinks help with hydration during intense exercise, while energy drinks are stimulants packed with caffeine and sugar. Knowing the difference can save your health and performance.
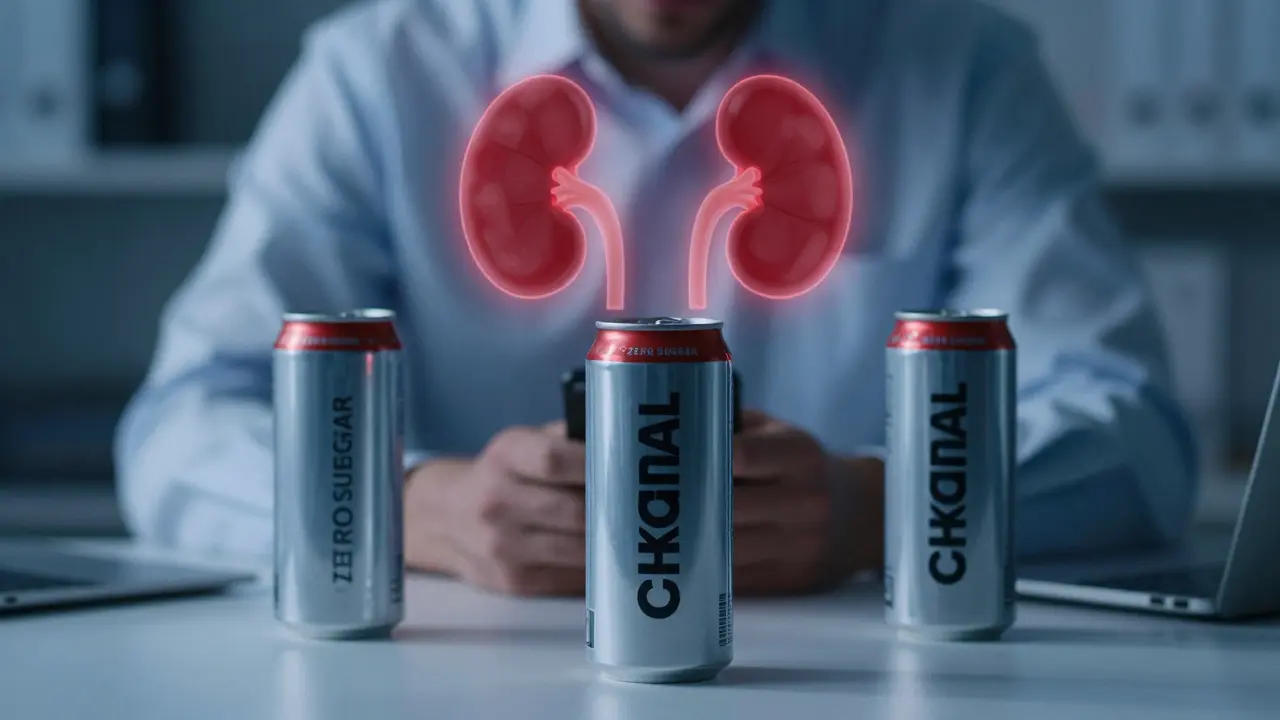
Zero sugar energy drinks may seem healthy, but daily consumption can strain your kidneys through artificial sweeteners, acids, and high caffeine. Learn the risks and how to protect your renal health.
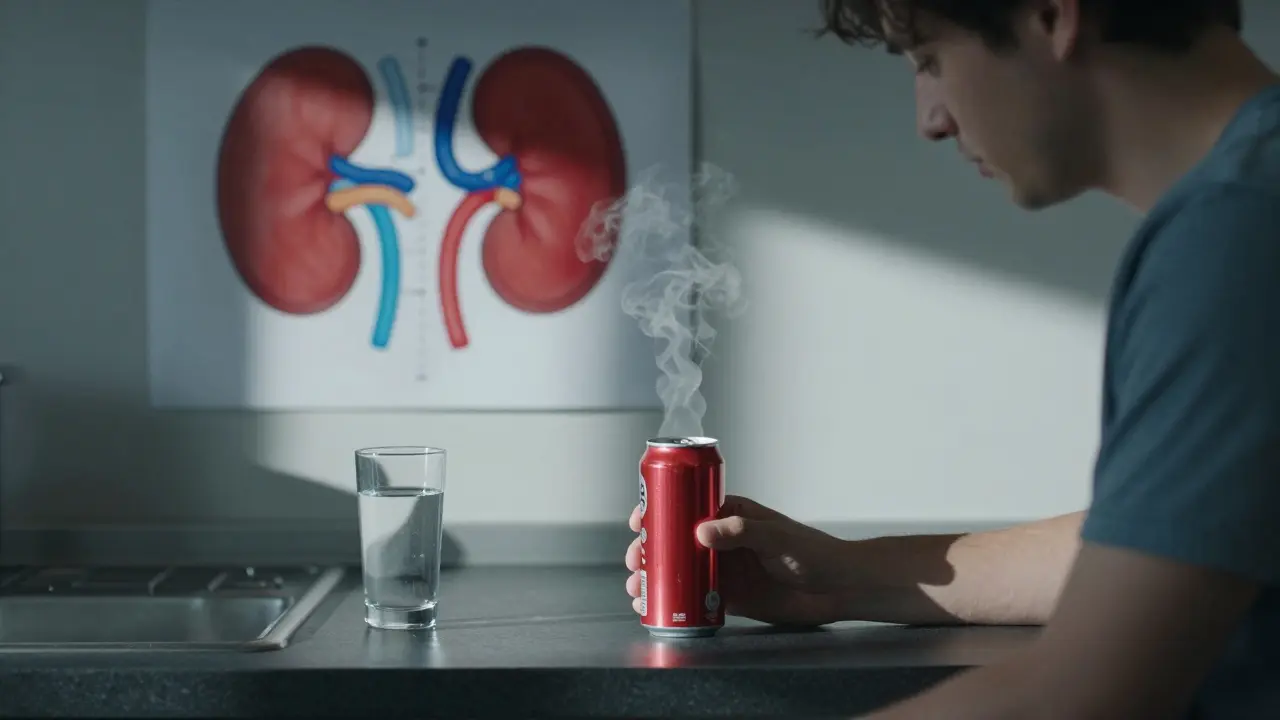
Energy drinks can stress your kidneys through caffeine, sugar, and dehydration. Regular use increases kidney stone risk and may cause long-term damage. Learn what science says and how to protect your kidneys.
Energy drinks overload your heart, liver, and kidneys with caffeine and sugar. The heart bears the biggest risk, but long-term use can cause lasting damage to multiple organs-even in healthy people.
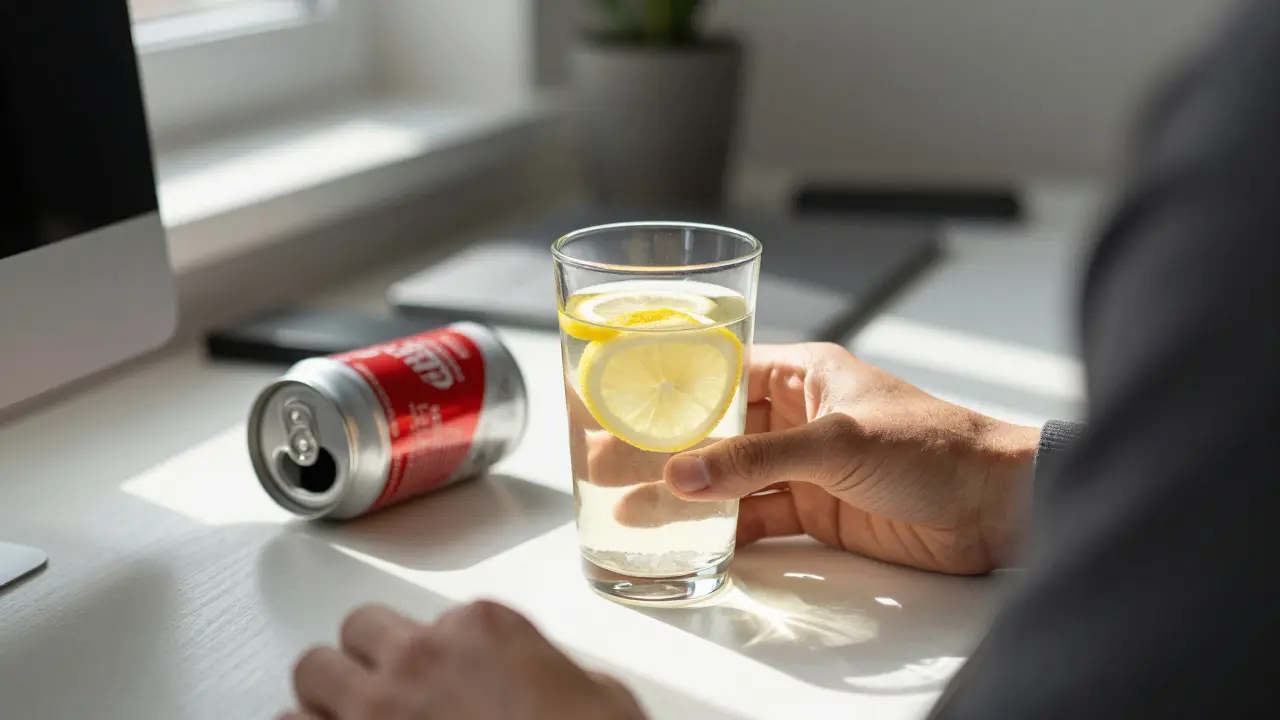
Swap your energy drink for water with sea salt and lemon to avoid crashes and boost real, lasting energy without sugar or stimulants. A simple change with big results.
Drinking four energy drinks a week may seem harmless, but the sugar, caffeine, and stimulants add up over time. Learn how this habit affects your heart, sleep, and metabolism-and what to drink instead.
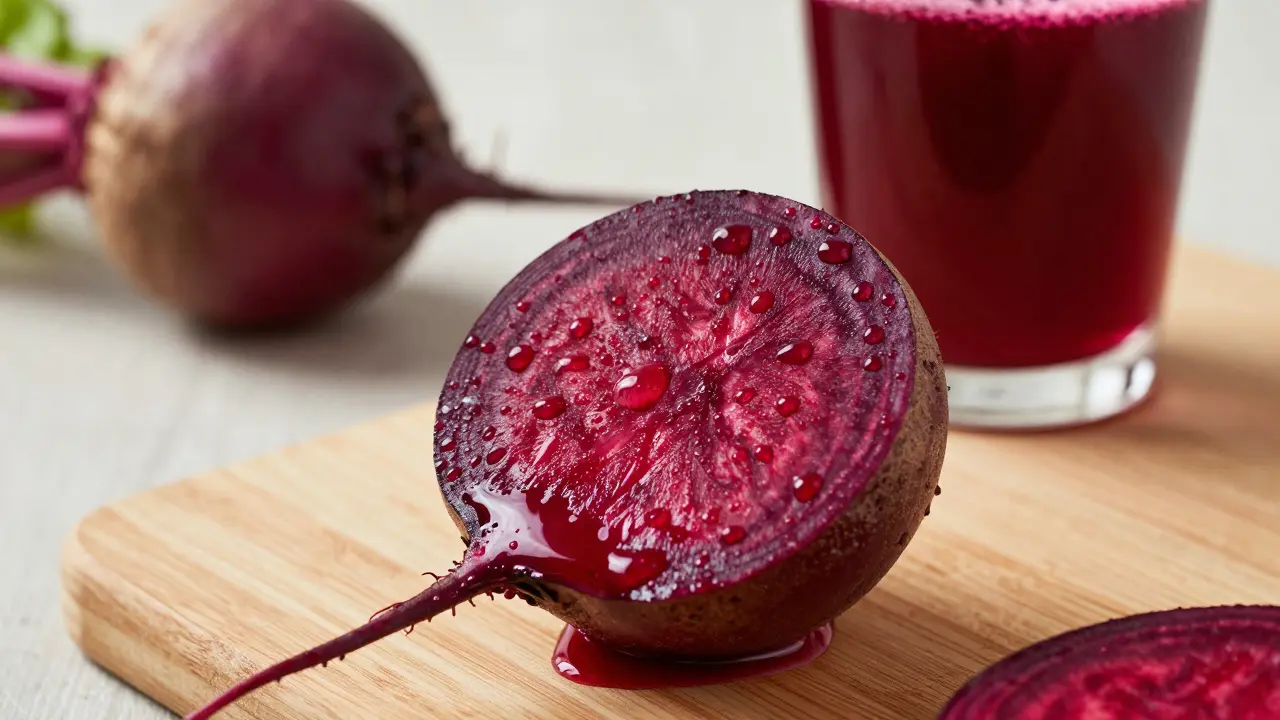
No energy drink truly opens arteries. While some contain ingredients like L-citrulline, the high caffeine and sugar content actually restrict blood flow. Real artery support comes from beetroot juice, green tea, and hydration.