Author: Amelia Starling
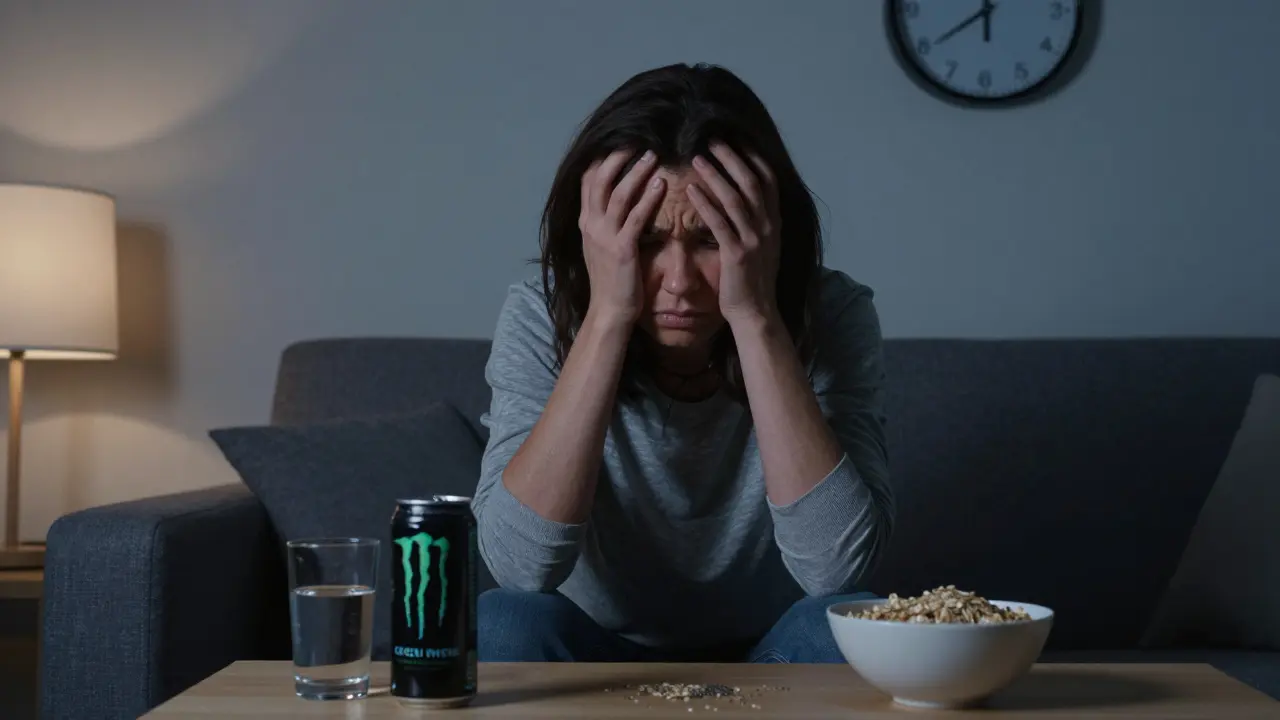
Caffeine from energy drinks can linger for hours, causing jitters and sleep disruption. Learn science-backed ways to help your body process it faster - and how to avoid overdoing it next time.
The healthiest energy drink for athletes is low in sugar, rich in electrolytes, and uses natural caffeine. Brands like Behold and Guayaki Yerba Mate lead the pack, while DIY coconut water options offer a clean, affordable alternative.
Discover the healthiest, science-backed alternatives to Red Bull in 2026-zero sugar, natural caffeine, and no crashes. Find out which energy drinks actually work without the junk.
Energy drinks may seem like a quick boost for athletes, but they're loaded with sugar, caffeine, and empty stimulants that hurt performance, hydration, and recovery. Here's why elite athletes avoid them.
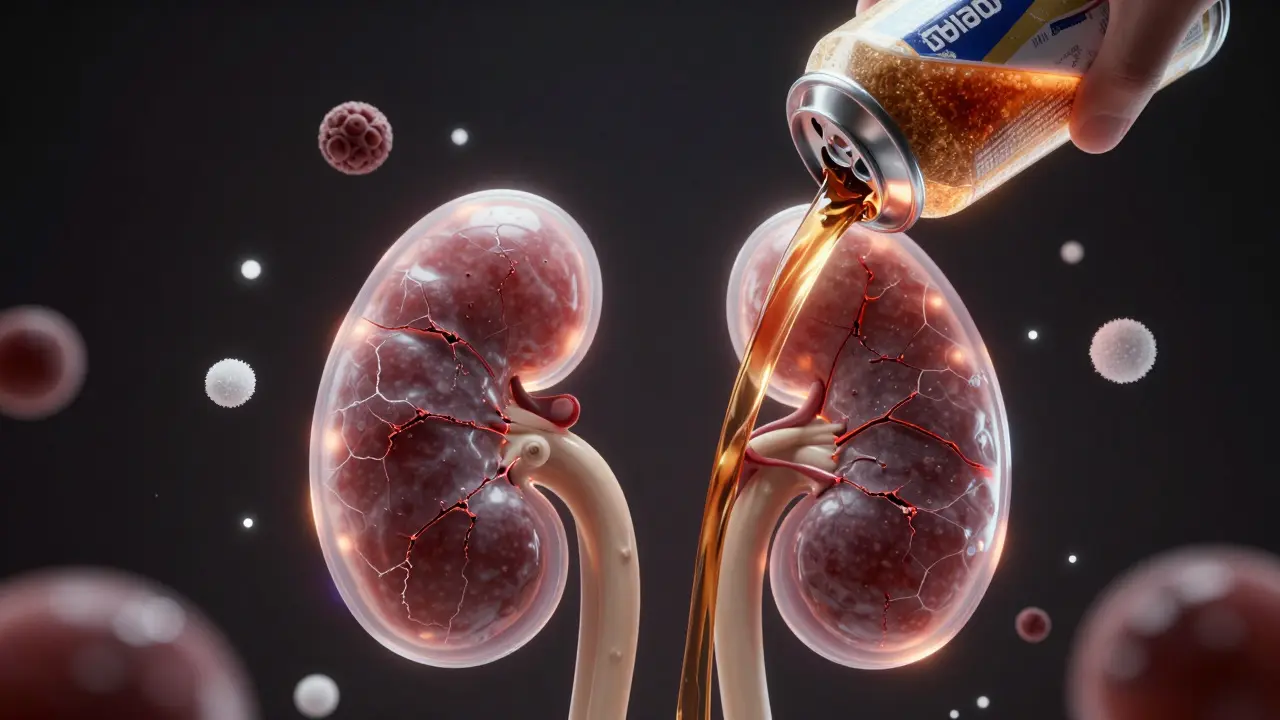
Energy drinks are one of the biggest hidden threats to kidney health, causing damage through high sugar, caffeine overload, and unregulated additives. Learn how they lead to kidney stress, acute injury, and long-term failure.
Energy drinks aren't safe for everyone. Teens, people with heart conditions, pregnant women, and those on certain medications should avoid them. Learn who's at risk and what to drink instead.
Energy drinks aren't just caffeinated beverages-they're specially formulated with stimulants like taurine, guarana, and high-dose B-vitamins to boost performance. Learn what truly qualifies as an energy drink and why most athletes avoid them.
Drinking a gallon of water a day sounds healthy, but it can be dangerous. Learn what science says about hydration, overhydration, and why energy drinks don’t make water intake safer - or smarter.
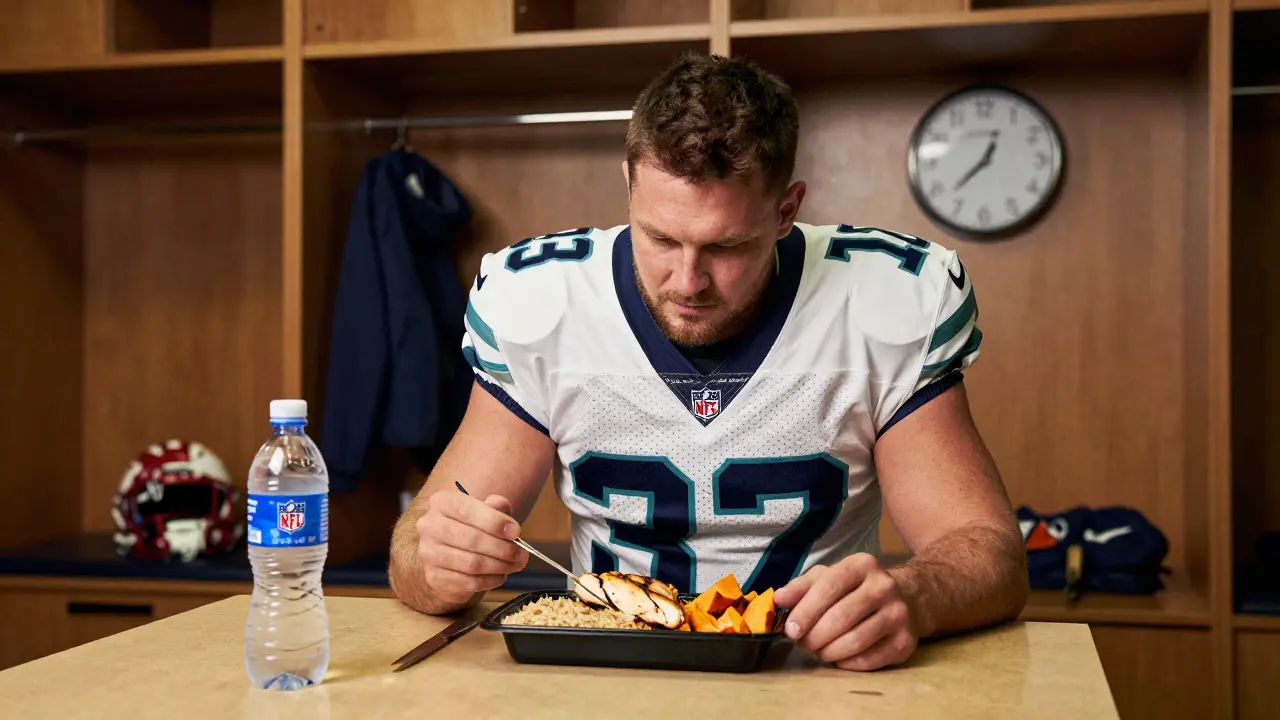
NFL players don't rely on energy drinks before games. Their pre-game meals focus on lean protein, complex carbs, and hydration-timed perfectly to maximize energy and avoid digestive issues. Here's what they actually eat.
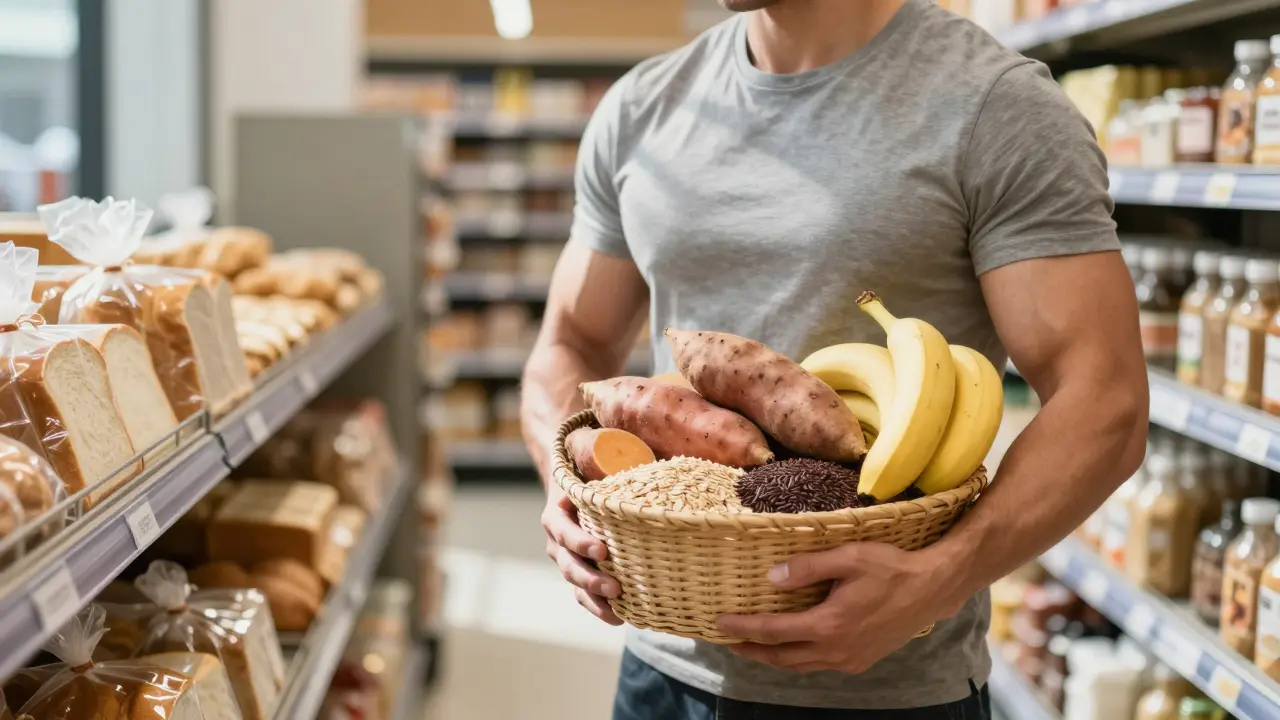
Bodybuilders avoid bread not because carbs are bad, but because most bread is refined, spikes insulin, and lacks nutrient density. They choose complex carbs like oats, sweet potatoes, and rice for better energy and muscle recovery.
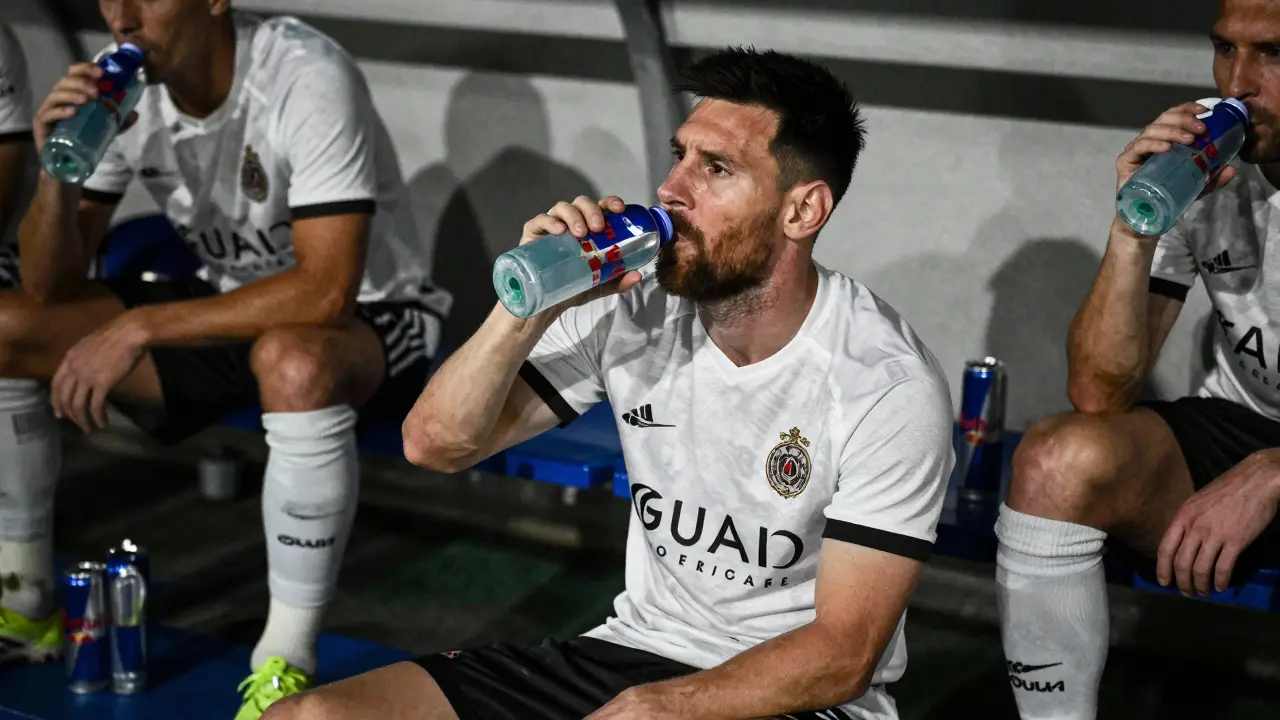
Most pro athletes avoid Red Bull due to its high sugar content and lack of performance benefits. Learn what they actually drink for energy, why caffeine works better in capsule form, and how to fuel like a pro without the hype.
Athletes should avoid sugary sodas, energy drinks, alcohol, and sweetened recovery shakes. These drinks hurt performance, delay recovery, and disrupt hydration. Simple, clean fluids like water and electrolyte solutions are far more effective.